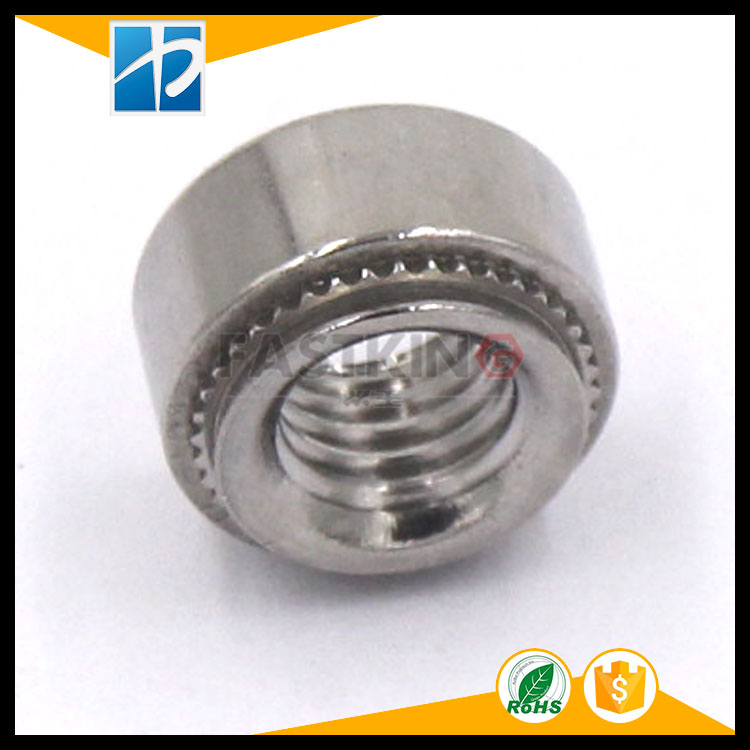
 1、Common types of metric rivet nuts:vS-M3-0、CLS-M3-0;S-M3-1、CLS-M3-1;S-M3-2、CLS-M3-2vS-M4-0、CLS-M4-0;S-M4-1、CLS-M4-1;S-M4-2、CLS-M4-2vS-M5-0、CLS-M5-0;S-M5-1、CLS-M5-1;S-M5-2、CLS-M5-2 
Dynamic diagram of rivet nut
2. Differences in the models of each rivet nut: Taking S-M3-1-ZC as an example
A. Material: S represents carbon steel, CLS represents stainless steel, and CLA represents aluminum
B. Tail code: Taking S-M3-1-ZC as an example
0 → 0.76MM (suitable for 0.8MM plates)
1 → 0.97MM (suitable for plates from 1.0 to 1.2)
2 → 1.37 (applicable to plates from 1.5 to 2.0)
(-0/-1/-2 are only codes for the tail code, and the specific values need to be checked by PEM. During production and inspection, we can check the packaging label to see if the rivet specifications are correct.)
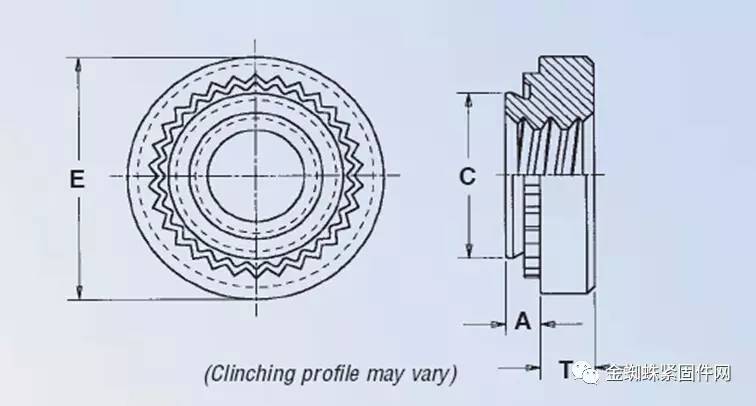
C. Riveting bottom hole:
The bottom holes of M2, M2.5, and M3 are all 4.3MM. The C value of the nut is 4.22MM
The bottom hole of M4 is 5.4mm, and the C value of the nut is 5.38mm
The bottom hole of M5 is 6.4MM, and the C value of the nut is 6.38mm
D. SP type rivet nut: specifically used for pressing stainless steel materials.
 3. British rivet nuts: such as S-632-0, S-832-1, etc. The representation method is the same as the metric system except for the thread specification. 4. Explanation of the representation method for rivet nuts, taking S-M3-1-ZI as an example: S-M3-1-ZI represents: 1. The material is carbon steel (ordinary steel) 2. Thread size is M3 3. -1 indicates that the A value of the nut is 0.97MM, suitable for products with a plate thickness of 1.0-1.2mm 4. Pressed rivet nuts with white zinc plated surface treatment Note: Handle code (0- applicable to plate thickness 0.8mm, 1- applicable to plate thickness 1.0-1.2mm, 2- applicable to plate thickness 1.5-2.0mm) 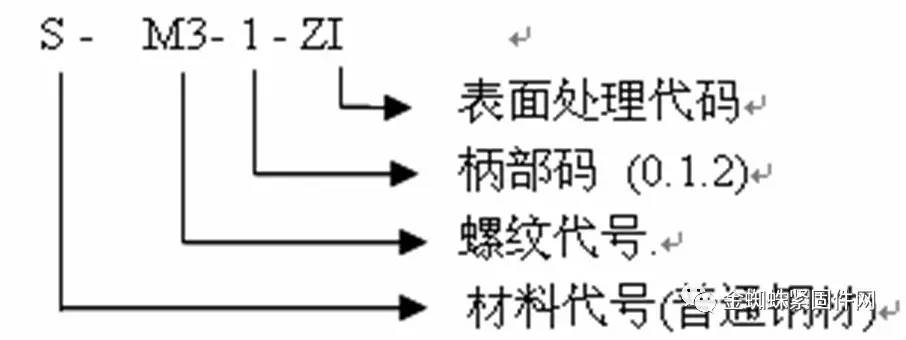 |
Contact: Mr. Deng
Phone: 13928071304
Tel: 0756-8586520
Email: lizhong@zhjiali.com
Add: 102, Building 4, No. 4 Fuyuan Road, Waisha Village, Shenwan Town, Zhongshan City, Guangdong Province,China